LoneStar Machines Running Mach3
PypeServer for Lone Star Machines Using Mach3 Controllers
Table of Contents
1 General overview of network layout 2
2 PypeServer Settings Overview 3
3 Mach3 Controller Settings 11
4 The Cut Program (.tap) File 11
4.1 Cut Program Folder Share 11
4.2 Loading and Cutting a Program 12
4.3 Partial Program example 13
General overview of network layout
PypeServer can be run from any Windows computer on a network. Users from different disciplines use PypeServer for different parts of the fabrication workflow. To allow these users access to PypeServer, the PypeServer SQL server needs to be on the company domain so that CAD programmers, Detailers, Shop Foremen and others can run the PypeServer application and access the SQL server. PypeServer also needs to connect to the machine's cut-program folder (where the .tap files go) with read/write access, so that PypeServer users can automatically place NC (.tap) cut programs into that folder.
The typical configuration looks like this:
Note: Internet connectivity also allows PypeServer support to assist in initial system configuration and ongoing support. PypeServer can work with your IT department to get PypeServer joined to the domain. For more IT-level information, see the PypeServer training document "Getting Started with PypeServer", section 2.
PypeServer Settings Overview
PypeServer support will help you getting your machine set up. This section explains the Machine and Torch settings, which you may from time to time wish to adjust.
Access the Machine & Torch settings in PypeServer by clicking on the gear icon in the upper right corner of the application. Many of the settings require Admin privileges. This is primarily to prevent accidental setting of parameters that could result in incorrect cutting of parts. By default, the Admin password is "Admin". If you wish to change it, please contact PypeServer support.
This section covers settings that PypeServer users should understand and may want to adjust over time. Numerous parameters are setup by PypeServer support and need not be addressed here.
Basic Machine Settings
NC File and PypeServer Part Status Synchronization
This section discusses how PypeServer can monitor files sent out to the machine to maintain the status of scheduled parts. For more information, please see the training video "NC File Management and Sync".
Scheduled Part status can be:
Not Nested
Nested
On Machine
Cut
Scrapped
These two machine settings are used to set status synchronization behavior.
Data Reporting Mode = <selection>
Data Reporting Mode = SystemWatchesFiles : With this setting, PypeServer will monitor the "Folder or IP Address" folder, such that
When files are deleted, the Scheduled Parts' status are changed from "On Machine" to "Cut".
When files are move to the subfolder: "Return To PypeServer Nested", the Scheduled Parts' status are changed from "On Machine" to "Nested"
When a user in PypeServer changes a pipe nesting that is currently "On Machine" back to nested, the NC file in the NC Programs folder (typically out at the machine) will be deleted.
This synchronization behavior is summarized in the following diagram:
Data Reporting Mode = None
With no data reporting (file tracking), users will need to manage the status of pipes after they are cut.
If this mode is selected, then the user can (should) maintain Scheduled Part cut status in PypeServer by selecting one or more pipes and selecting the Change Status button as shown here:
Note that this is extra work that is performed automatically when Data Reporting Mode = SystemWatchesFiles.
Other settings are not applicable:
The Data Reporting Mode = Automatic is for machines directly connected to PypeServer, where there is no file transfer occurring. This is not currently applicable to the Mach3 controls, but is under investigation.
The Data Reporting Mode = DialogProcess selection is for manual saws.
NC File Timer Interval Seconds = <minutes>
When you use this synchronization feature, you can set how often the system checks the NC file folder for synchronization. This setting is in the System Properties Tab and is a global setting for all machines, shown here:
For more information, please see the training video "NC File Management and Sync".
Last Cut on End of Pipe "Use Far Pipe End"
PypeServer can nest parts so as to use the far end of the pipe as the final (straight) cut of the last part. To use this feature:
One-Time Setup: (PypeServer can help you with these settings.)
Enter the Machine Setting: "Dead-Zone" distance. More on that below.
Enter the Machine Setting: "Machine Zero To End of Pipe" distance as a negative number.
Each pipe or Default Nesting Setting
You must check the "Use Pipe Far End" on the Pipe. Checking this will change the Dead-Zone indicator to green and PypeServer will nest parts into that zone. You can also set this as a default in the Nesting Settings dialog that can be opened from the Nesting Tab.
Each Pipe:
You must make sure no cuts go into the Dead-Zone
One configuration of nesting with the Far Pipe End looks like this:
Note: As mentioned above, you can also check the Use Far Pipe End checkbox in the Nesting Settings dialog so that all new Pipes will have this checked.
Machine Setting: Cutting Dead Zone
When you nest with "Use Far Pipe End" checked, the dead zone will become green to indicate that you can nest in it. However, PypeServer still needs to know the length of this Cutting Dead Zone.
Cutting Dead Zone is the closest the torch can get to the pipe end when it's in the chuck. Be sure to consider restrictions due to steep beveling.
When not using the far pipe end ("Use Far Pipe End" unchecked), then this dead-zone will show up in PypeServer as a yellow area on the end of the pipe and PypeServer will not nest into it. It will look like this:
LeadIn/Out Settings
These settings are seldom changed. These are only limits. The actual leadin settings are made in the Torch settings, but they must fall within these limits.
For more information, please see the document "Torch End of Cut Leadout and Tuning" in the PypeServer training system.
Leadin Min Distance = <distance>
This is the minimum distance allowed for a leadin in PypeServer. A good performing machine can have a short leadin.
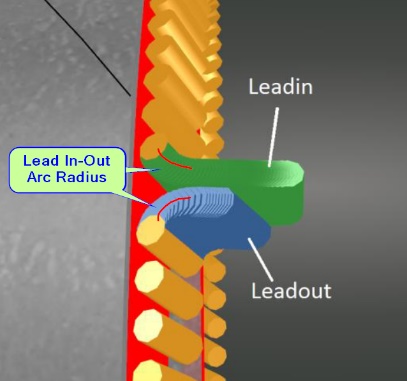 Lead In-Out Arc Radius = <distance>
Lead In-Out Arc Radius = <distance>
This is the radius of the turn made by the leadin. Note that this is not the overall length of the leadin. Having this as a small radius decreases the range of gouging, but the tradeoff is that if it's too tight, the machine may fault or have difficulty making turn smoothly.
Leadin Steps = <integer number>
This is the number of steps PypeServer creates for the leadin. This adjustment is not typically made by the user.
Is Metric = <checkbox>
If you set this to Metric, all your machine and torch settings will be interpreted as metric. You can still have standard (Imperial) measurements parts. Note that you do not need to set this to Metric just because your machine runs in metric. This is only a convenience to allow users to work in familiar units.
Add Date Time To NC Files
When true, nc files will look like this: Part 96 11_30_21 17_50.nc
When false, nc files will look like this: Part 96.nc
Stagger Straight Cut Start Rotation Dist = <distance>
When straight cuts are nested together without any rotation between starts and finish, the leadins and leadouts can overlap and cause the torch to burn incorrectly or fault as the leadin torch start hits the leadin and leadout gaps of the previous cut. This instructs PypeServer nesting to rotate the next part by a distance (around the pipe) so as to avoid this intersection. Shown below is a 4.5" pipe with StaggerStraightCutStartRotationDist = 1 inch.
Machine Properties
This section covers additional machine settings you will find in the right-pane of the Machine Settings dialog.
Torch Settings
 Torch Properties
Torch Properties
This section covers additional Torch settings you will find in the right-pane of the Torch Settings dialog.
These will be unique for each type of torch you use on your machine-such as Plasma, Gas, Etch etc.
| Name | Description | Default Value1 |
|---|---|---|
| Cut Height | The Z height above the part for cutting | 0.2 |
| Dynamic Z Height | When true and when beveling, the machine will adjust Z-Height to keep the torch up off the pipe by at least the "Tip Edge Min Interference Dist" property. | False |
| Fixed Pipe Holes | For no-bevel holes, and if mechanically possible, the pipe will be fixed and the torch will move about the pipe to cut the hole. | True |
| Max Feed Rate | Max Feedrate allowed. This is set to limit the B-axis tilt rate because the feedrate becomes large when the motion is primarily the torch tilting. |
3000 |
| Pivot Z from Torch Tip | This is the Z distance from the tip of the torch to the torch's B rotational (tilting) axis. If the tilt/pivot axis is right at/on the torch tip, set this to zero. If the pivot axis is below the torch tip by 0.1 inch, set this value as negative: -0.1 inch. |
0 |
| Tip Edge Min Interference Dist | When using Dynamic Z Height, this is the closest the torch tip is allowed to get to the pipe. | 0.5 |
| Torch Control Type | Specifies the torch controller type when "Use Torch Control" is true | Varies |
| Torch Start Dwell Secs | Machine pause/dwell time after the torch is turned on. When adjusting this, consider the time the torch spends traveling from Z Pierce Height to Cut Height. You may need to change this for different pipe thicknesses. Pierce should occur at the pierce point, but not dwell too long or it will cause wear on the consumables. |
0.75 |
| Torch Tip Base Diameter | Diameter measured across the torch tip. Used with Dynamic Z Height to prevent the torch from getting too close to the pipe when beveling. | 0.4 |
| Transfer Height | Z height for the torch when moving to the start of the cut program and when moving to a final position at the end of the program | 2 |
| Use Torch Control | When true, the Torch Controller will be used for kerf and feedrate lookups, and any other automations supported by the given torch controller and the Mach 3 controller. | False |
| Z Down to Cut Height Feedrate | Feedrate to move from Pierce Height to Cut Height. | 50 |
| Z Pierce Height | The Z height for piercing. This is typically set higher than the cut height. |
0.3 |
| Z Retract Height | Torch height when moving between cuts. | 2 |
Mach3 Controller Settings
The following screenshot was provided by Lone Star. Settings may be different for your machine. The highlighted setting has enabled the machine to run smoothly through g-code steps. If your machine is not running with a smooth speed through cuts, please make sure the highlighted item is checked.
This dialog can be found by navigating to the upper left hand menu named "Config". Then select "General Config" in the sub menu.
The Cut Program (.tap) File
For LoneStar Machines running Mach3, PypeServer outputs to a numerical control (NC) G-Code format, as a .tap file. If you use a different suffix, you can change that in the Machine Settings.
Mach3 programming documentation covers the NC codes used in the PypeServer output files, and the output file explains many of the steps in comments.
Cut Program Folder Share
PypeServer writes the .tap cut files to a folder specified in the Machine Settings "Folder or IP Address" property. This folder should be shared read/write between the PypeServer computer that creates the NC files, and the Mach3 machine. This folder is typically on the LoneStar Machine computer.
Loading and Cutting a Program
Loading a program
Load <PypeServer Created>.tap files with the "Load-GCode" button in the Mach3 application.
Navigate to where the NC file is located and open the file
Once loaded, read the instructions in the NC file. It will tell you where to start the torch. In normal operations this start is just in from the edge of the pipe end where cutting is starting.
Running a program
To start a program, click on Cycle Start,
You will then be asked in a dialog "Move To X and Y Zero and Save Location". ALWAYS click No on this because PypeServer manages machine location.
Per machine configuration and programming there are times when the machine will pause when running a program. Reasons to pause include the removal of small pieces or scraps, before returning to the start position, or changing a torch (if that is allowed). In all cases, ALWAYS click No to continue after a pause or the machine will lose its working position.
Partial Program example
The following is the beginning of a sample .tap file for a single part (not a nesting). The initial commands will vary based on numerous features in PypeServer.
(Filename: Part 438.tap)
(Date Created: 8/5/2022)
(******* Program Start Instructions *******)
(Position the torch on the end of the pipe by at least 0.22 inches )
(Set torch about an inch above the pipe.)
(ALWAYS select No to start program or continue.)
(NEVER re-zero when you continue.)
(******* Program Start Instructions *******)
G20 G90 G40
G52 Y0. Z0. A0.
G92.1
G92 Y0.0000 Z0.0000
(**************** New Cut *****************)
(Design 438)
(Miter Cut 2842)
G00 Z1.
G01 B0. F3000.
G00 X0. A-0.0110 Y0.2845
M200
G00 Z0.15
(With no leadin, tilt first so you don't damage the cut.)
G01 B-37.5 F3000.
M03
G01 Z0.2 F50.
G01 F80.
G01 A-2.3200 F1913.46
G01 A-357.7000
G01 A-359.9900
M05
G00 Z1.
?
If machine is metric, then default values will be converted to metric equivalents??
Related Articles
NC Code for Vernon Machines
NC Code for Vernon Machines PypeServer for Vernon Machines This document covers topics specific to Vernon machine working well with PypeServer. Topics include: General network layout for using PypeServer with the machine Vernon MPM settings and ...Getting Started with HGG Machines
Getting Started with HGG Machines PypeServer for HGG Machines This document covers topics specific to HGG machine working well with PypeServer. Topics include: General network layout for using PypeServer with the machine HGG ProCAM settings and ...Pypeserver with EdgeConnect Machines
Pypeserver with EdgeConnect Machines PypeServer with EdgeConnect machines Machine configuration When configuring your machine, some preparatory steps are required in order to get meaningful test results. Getting axial directions correct This is done ...Checks for Running PypeServer Remotely
Checks for Running PypeServer Remotely Basic Checking for Running PypeServer Across the LAN On Kiosk Make Sure the remote seat firewall is not blocking the connection between the two computers.? Check if the firewall is on. It must either be off, or ...Enterprise Training - Machine Operation
Make a single cut on the pipe Trim the pipe with a single Miter cut. Click a button when you need to make a single straight or miter endcut on the pipe. v2.16 13 Beam Divergence Beam Divergence defined and how to set What beam divergence is and how ...